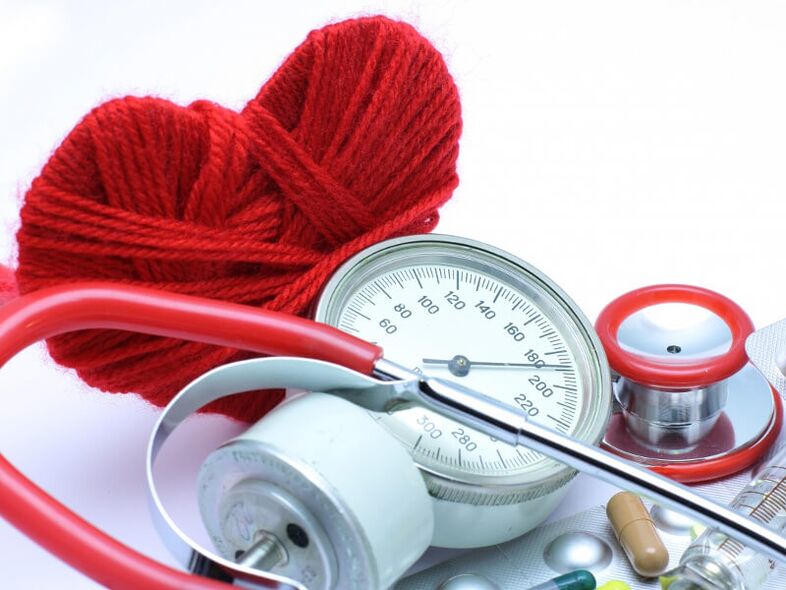
Hypertension is the most common disease of the cardiovascular system.
Hypertension is rapidly "younger", and today it is not only a disease of the elderly, but also frequently occurs in pregnant women and is becoming more common among adolescents.
What is arterial hypertension? The answer to this question can be found in the definition of this disease state.
It is characterized by chronically elevated blood pressure, with the highest (systolic) value above 140 mm Hg and the lowest (diastolic) above 90 mm Hg. In people in a calm state, at least three measurements were taken at different times.
The optimal blood pressure indicator is 120-130 per 80-89 mmHg, if it is higher, aggressive treatment of high blood pressure needs to be started. However, few people are able to diagnose the disease early: about 35% of men and 55% of women are aware of their high blood pressure, and only half of them are involved in the treatment of arterial hypertension, compared with 6% of men and 20% of women. The female population controls their own stress.
The earlier arterial hypertension is detected and controlled, the lower the risk of future hypertensive complications (ischemic disease, atherosclerosis, kidney disease, low testosterone levels in the blood, erectile dysfunction).
High blood pressure may be one of the causes of male impotence.
Note it is useful
The main task in the treatment of high blood pressure is to keep the blood pressure under control to avoid more serious health problems, because the disease cannot be completely cured.
what is dangerous high blood pressure
With prolonged high blood pressure, the walls of blood vessels thicken and lose their ability to relax, which prevents normal blood supply, saturating tissues and organs with oxygen and other nutrients and reducing their functional activity. Let's consider what dangerous high blood pressure is in more detail:
- Hypertensive crisis- The most common exacerbation of arterial hypertension, which can occur both in the patient's relative satisfaction and as a result of the patient's psychophysiological stress. Hypertensive crisis develops at high speed, causing a sharp rise in blood pressure, leading to severe headache, dizziness, tachycardia or arrhythmia, nausea and vomiting. At risk are those suffering from weather dependence who are in a pre-climate period.
- myocardial infarction- Concurrent hypertension can occur within minutes and lead to death. The main symptom is prolonged pain episodes.
- stroke- Circulatory disturbances in the blood vessels of the brain, cerebral hemorrhage, characterized by a sudden severe headache, soon followed by other symptoms from the brain: speech disturbance, twisting of the mouth, paralysis of a certain part of the body. This process is reversible if emergency measures are taken and capillary bleeding is performed in the presence of hypertension.
- angina pectoris- The disease is not so short-lived. Violating the heart can lead to severe emotional overload, overwork. Accompanied by severe chest pain, feeling unwell, can cause frequent vomiting.
- heart failure- Chronic disease of the heart muscle, which is unable to supply oxygen to the organs and tissues of the body. It is characterized by the patient's complete weakness and inability to tolerate basic physical activities: independent weightlifting, walking, etc.
- coronary artery disease- Insufficient blood supply to the coronary arteries, resulting in insufficient nutrition of the heart. Careful adherence to the prescribed treatment of hypertension is not difficult to avoid the development of coronary heart disease.
- Renal Failure- Impaired kidney function, destruction of neurons, partial inability to remove toxins from the body. Arterial hypertension is the second cause of acute or chronic renal failure after diabetes.
- Distorted vision- Occurs due to impaired blood supply to the retina and optic nerve. A sharp rise in blood pressure can cause the arteries supplying the optic nerve to spasm, compromising the integrity of retinal blood vessels. High blood pressure is dangerous for diseases such as retinal or vitreous hemorrhage: the first causes black spots to form in the visual field, and the second causes vision loss in the affected eye.
To avoid any dangerous complications of hypertension, it is necessary to consult a doctor promptly and carry out an examination, which will help determine the stage of development of the disease and prescribe the required treatment.
Degree of Hypertension: Classification, Forms
Numerous classifications of hypertension are used depending on the nature of one or more criteria assessments.
Assign developmental stages such as origin, form of leakage, blood pressure levels, and extent of target organ damage.
The first task of diagnosing arterial hypertension is to distinguish the nature of the disease. There are two categories here:
- Essential or essential hypertension - elevated blood pressure is the underlying cause;
- Secondary or symptomatic arterial hypertension - Hypertension is caused by disease in other organs or systems: kidneys, heart, endocrine glands, lungs, thyroid.
According to experts
Symptomatic high blood pressure cannot be treated and started with it without treating the disease that causes it. In some cases, high blood pressure also goes away as the underlying disease goes away.
In addition, blood pressure may increase until hypertensive crisis due to improper intake of certain drugs, neurosis, excessive use of caffeine and other stimulants.
When diagnosing essential hypertension, doctors usually classify the disease according to high and low blood pressure in order to choose the right strategy for treating essential hypertension. Internationally, high blood pressure is divided into three grades:
- 1 degree high blood pressure- Systolic 140-159 mmHg, Diastolic 90-99 mmHg. A mild form of the disease, characterized by sudden changes in blood pressure that either normalizes on its own or rises again.
- high blood pressure 2 degrees- Systolic 160-179 mmHg, Diastolic 100-109 mmHg. In the moderate form, the pressure builds up for a longer period of time and rarely drops back to normal.
- high blood pressure 3 degrees- Systolic blood pressure above 180 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure above 110 mmHg. The form is serious, the pressure is stable at the level of pathological indicators, the complications are serious, and medication is difficult to correct.
Additionally, isolated systolic hypertension is isolated and occurs in approximately one third of older adults with arterial hypertension. This form is due to age-related loss of large vessel elasticity and is often associated with myocardial infarction, coronary heart disease, congestive heart failure, and left ventricular hypertrophy. Blood pressure indicators: Systolic blood pressure up to 160 mmHg. and above, diastolic blood pressure - below 90 mmHg.
useful information
Of note is another small group - the so-called "white coat hypertension", in which a person's blood pressure rises only when measured by medical staff, under the influence of psycho-emotional factors. In this case, the diagnosis is confirmed by repeated measurements of stress in a calm home environment.
In addition to the degree of hypertension, at the time of diagnosis, risk factors that may contribute to complications of the cardiovascular system and stages of the clinical course of the disease are also assessed:
- Transistor (initial) hypertension. Increases in pressure are periodic and return to normal values; no blood pressure lowering drugs are used.
- unstable high blood pressure. Elevated blood pressure is directly related to predisposing factors: stress, severe psychological or physical stress. To stabilize the pressure, medication is required.
- stable arterial hypertension. Stress continued to increase with severe supportive therapy.
- malignant form. Increase stress to very high levels and the disease can progress rapidly and lead to the development of serious complications.
- crisis table. Periodic hypertensive crises against a background of normal or slightly elevated pressure are characteristic.
The severity of hypertension and possible risk of complications can be assessed only on the basis of a thorough examination: general and biochemical examination, ultrasonography of the heart and other organs, electrocardiogram, fundus examination. Patients with arterial hypertension are usually thoroughly examined during hospitalization.
High blood pressure is the main warning symptom of high blood pressure in both men and women.

Symptoms of high blood pressure may disappear in the long term, and if a person does not use a tonometer regularly, he can learn about his disease and have begun to treat its complications.
Often high blood pressure has no manifestations at all, except for its main symptom, persistent high blood pressure.
Also, the concept of "persistent" or "chronic" is key here, because in many situations (stress, fear, or anger), stress increases and then returns to normal on its own.
However, few people can manage their stress levels, so you should be aware of the following symptoms that indicate the development of arterial hypertension:
- Headache. Most commonly found on the occipital bone, parietal lobe, or temple. It can happen at night and immediately after waking up. Usually, it increases with mental or physical exhaustion. Sometimes there is swelling of the eyelids and face.
- Dizziness. Sometimes even with little physical effort: coughing, turning or tilting the head, rising sharply.
- Pain in the heart area. Not only can it happen during times of emotional stress, but also during rest. Long-term pain, squeezing pain, and short-term tingling are all possible. Do not go away after taking nitroglycerin.
- Strong heartbeat.
- There is a noise in the ear.
- Visual impairment: veils, fog, "flies" in front of you.
- Arterial disease: cold extremities, intermittent claudication.
- Leg swelling. Indicates impaired renal excretory function or heart failure.
- Difficulty breathing. It occurs during physical exertion and rest.
Important to know
Hypertensive crisis - an emergency caused by high blood pressure levels, also classified as symptoms of 2nd and 3rd degree hypertension. At the same time, in patients with grade 1 arterial hypertension, the unpleasant symptoms of the disease can be completely disappeared by strictly following the doctor's advice and following the diet of hypertensive patients.
It cannot be said that there is a significant difference in the symptoms of high blood pressure between men and women, but it is true that men are more likely to develop the disease, especially in the 40 to 55-year-old age group. This is partly due to differences in physiology: Men and women, unlike women, are each heavier and have a significantly higher volume of blood circulating in their blood vessels, which creates favorable conditions for high blood pressure.
On the other hand, women are more responsible for their own health and proper lifestyle. Men reported more stressful situations at work, drinking and smoking, but this was no longer a symptom of high blood pressure, but a cause of its development.
Treating high blood pressure with drugs and folk remedies
Treatment of high blood pressure and other diseases that are difficult to diagnose and require ongoing treatment (diabetes, allergies, prostatitis and impotence) should be written and prescribed only by specialists. Hypertension medication will be prescribed if restricting food, salt intake, avoiding alcohol and smoking, avoiding stress and other correctable causes of high blood pressure do not help normalize blood pressure levels.
When treating high blood pressure with folk remedies, there are usually no side effects. You don't have to run to the pharmacy for an expensive drug or wait in line for the doctor to write another prescription. All you have to do is take a moment to yourself, change your diet, and learn how to manage stress.
Causes of high blood pressure and the development of high blood pressure
The etiology of arterial hypertension is not fully understood, and both internal systems and external factors of the body play an important role in the development of the disease.
The main cause of high blood pressure is impaired circulation through the blood vessels, restricting blood flow to the left ventricle of the heart. In modern medicine, there is a perfectly logical explanation for this - the structural changes in blood vessels with age, the formation of blood clots and atherosclerotic plaques in the lumen.
If in symptomatic hypertension the cause of hypertension is caused by other diseases, then in essential hypertension, which is present in 85% of cases, the exact cause of hypertension cannot be determined, it occurs independently.
There are a number of risk factors that contribute to persistently elevated blood pressure, and they are often thought to be the cause of high blood pressure. These include:
- Age, men over 55 years old, women over 65 years old. With age, the walls of blood vessels lose elasticity, increasing resistance to blood flow, and as a result, pressure increases.
- Genetic predisposition.
- ground. As mentioned earlier, men are more likely to develop high blood pressure.
- Violation of fat metabolism, obesity (waist circumference over 102 cm in men, women - over 88 cm).
- diabetes.
- smokes. It causes an immediate increase in blood pressure, and smokers with years of experience are prone to vascular disease.
- Abuse of alcohol. Abstainers' blood pressure dropped by at least fifteen points.
- Too much salt intake. Excessive intake of sodium (the main component of table salt) is one of the most important causes of high blood pressure in hypertensive patients: Sodium chloride blocks fluid excretion, increasing the patient's already high blood vessel tone. Remember that the average person consumes three times as much salt as he needs, learn not to add salt to your food.
- Lack of physical activity and a sedentary lifestyle.
- Under pressure.
- Disrupt cholesterol metabolism.
- Insufficient potassium intake in the diet.
- Elevated levels of epinephrine in the blood.
- Congenital heart defects.
Various kidney diseases, late-stage poisoning in pregnant women, frequent use of certain drugs, and in some cases oral contraceptives, are to blame for secondary hypertension.
The above risk factors can be divided into two categories:
- It can be eliminated on its own or with the help of a doctor: treatment of obesity, reduction of blood cholesterol levels, amount of smoking, alcohol or salt intake, weight loss, etc.
- Avoid It's Impossible: Age and Genetic Predisposition.
Therefore, people in the so-called second-highest-risk group need to carefully monitor their health to control and prevent high blood pressure. For everyone with at least one of the above factors, constantly monitor blood pressure levels and, of course, lead a normal and active lifestyle.